Tate Britain Staircase
Tate Britain (known from 1897 to 1932 as the National Gallery of British Art and from 1932 to 2000 as the Tate Gallery) is an art museum on Millbank in London. It is part of the Tate network of galleries in England, with Tate Modern, Tate Liverpool and Tate St Ives. It is the oldest gallery in the network, having opened in 1897. It houses a substantial collection of the art of the United Kingdom since Tudor times, and in particular has large holdings of the works of J. M. W. Turner, who bequeathed all his own collection to the nation. It is one of the largest museums in the country.
The gallery is situated on Millbank, on the site of the former Millbank Prison. Construction, undertaken by Higgs and Hill,[3] commenced in 1893, and the gallery opened on 21 July 1897 as the National Gallery of British Art. However, from the start it was commonly known as the Tate Gallery, after its founder Sir Henry Tate, and in 1932 it officially adopted that name.[4] Before 2000, the gallery housed and displayed both British and modern collections, but the launch of Tate Modern saw Tate's modern collections move there, while the old Millbank gallery became dedicated to the display of historical and contemporary British art. As a consequence, it was renamed Tate Britain in March 2000.
The front part of the building was designed by Sidney R. J. Smith with a classical portico and dome behind, and the central sculpture gallery was designed by John Russell Pope. Tate Britain includes the Clore Gallery of 1987, designed by James Stirling, which houses work by J. M. W. Turner. The Clore Gallery has been regarded as an important example of Postmodern architecture, especially in the use of contextual irony: each section of the external facade quotes liberally from the building next to it in regard to materials and detailing.[5]
Crises during its existence include flood damage to work from the River Thames, and bomb damage during World War II. However, most of the collection was in safe storage elsewhere during the war, and a large Stanley Spencer painting, deemed too big to move, had a protective brick wall built in front of it.
In 1970, the building was given Grade II* listed status.[6]
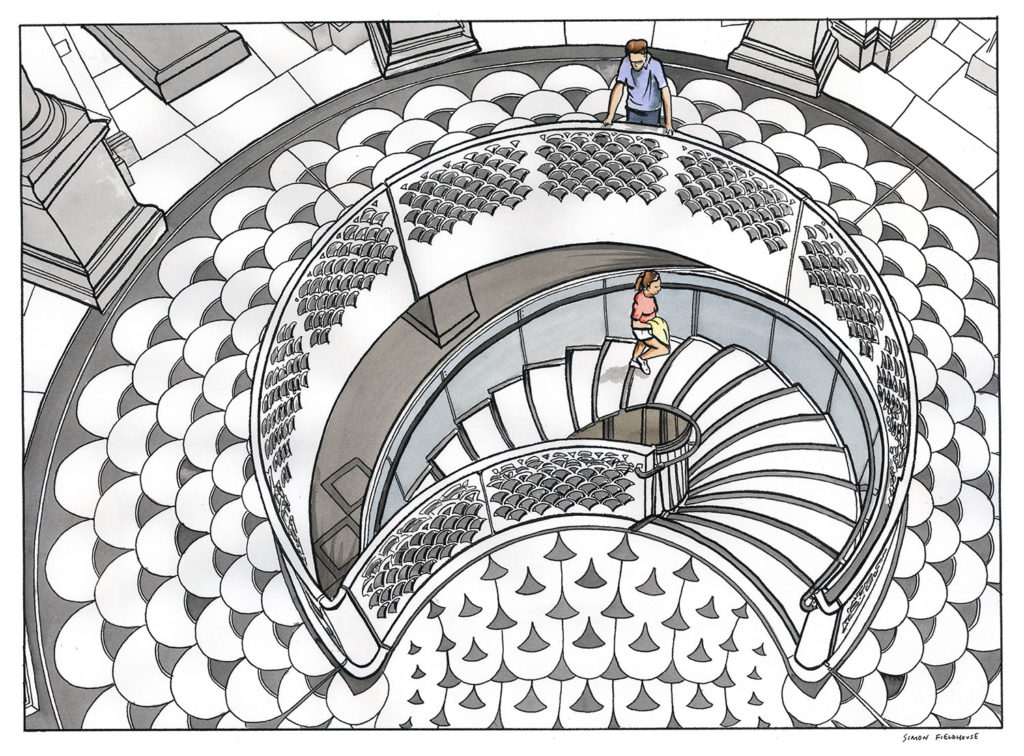
In 2012, Tate Britain announced that it had raised the £45 million[7] required to complete a major renovation, largely thanks to a £4.9 million grant from the Heritage Lottery Fund and £1 million given by Tate Members.[8] The museum stayed open throughout the three phases[9] of renovation.[7] Completed in 2013, the newly designed sections were conceived by the architects Caruso St John and included a total of nine new galleries, with reinforced flooring to accommodate heavy sculptures. A second part was unveiled later that year, the centrepiece being the reopening of the building's Thames-facing entrance as well as a new spiral staircase beneath its rotunda.[9] The circular balcony of the rotunda's domed atrium, closed to visitors since the 1920s, was reopened. The gallery also now has a dedicated schools' entrance and reception beneath its entrance steps on Millbank and a new archive gallery for the presentation of temporary displays.[10]