The Vanderfield Building Royal North Shore Hospital (RNSH) is a major public teaching hospital in Sydney, Australia, located in St Leonards. It serves as a teaching hospital for Sydney Medical School at the University of Sydney and has approximately 600 beds. It is the referral hospital for Northern Sydney. Its primary referral area accommodates 5.7% of the Australian population or 17% of the NSW population.
The Royal North Shore Hospital (RNSH) is a leading tertiary teaching hospital of The University of Sydney (medicine, allied health), the Sydney University of Technology (nursing), and the Australian Catholic University. It is also a major Trauma Centre which provides specialised services in the areas of severe burns, neonatal intensive care, spinal cord injury and interventional radiology. The Kolling Institute of Medical Research is a health and medical research centre with a focus on research training.
It began as a cottage hospital located in Willoughby Rd, Crows Nest. The foundation stone was laid by Sir Henry Parkes, 18 June 1887. The hospital was opened with accommodation for fourteen patients, with the requisite office and rooms for the medical and nursing staff. Medical staff numbered four honorary doctors and nursing staff numbered five. The site of the original hospital was bounded by Willoughby Rd., Albany and Holterman Streets and Zig Zag Lane. The old site is now a busy part of the commercial centre of Crows Nest.In 1902, it opened on its current site at St Leonards, with 48 beds available for patients. New departments and wards were added over the next fifty years, reflecting the increasing diversity and professionalisation of health care. Between 1935 and 1940, Polio treatment pioneer Sister Kenny Kenny travelled extensively throughout Australia helping to set up clinics. In the mid-thirties, she set up one of her pioneering clinics at RNSH. In 1940, the New South Wales government sent Kenny to America to present her clinical method for treating polio victims to American doctors.
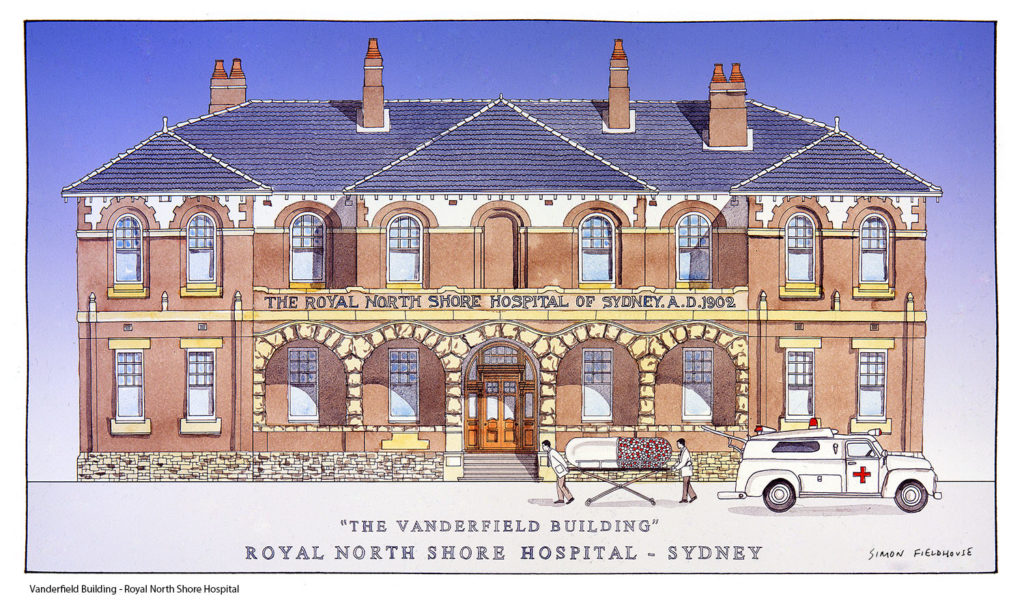
Vanderfield Building RNSH
The Vanderfield Building Royal North Shore Hospital (RNSH) is a major public teaching hospital in Sydney, Australia, located in St Leonards. It serves as a teaching hospital for Sydney Medical School at the University of Sydney and has approximately 600 beds. It is the referral hospital for Northern Sydney. Its primary referral area accommodates 5.7% of the Australian population or 17% of the NSW population.
The Royal North Shore Hospital (RNSH) is a leading tertiary teaching hospital of The University of Sydney (medicine, allied health), the Sydney University of Technology (nursing), and the Australian Catholic University. It is also a major Trauma Centre which provides specialised services in the areas of severe burns, neonatal intensive care, spinal cord injury and interventional radiology. The Kolling Institute of Medical Research is a health and medical research centre with a focus on research training.
It began as a cottage hospital located in Willoughby Rd, Crows Nest. The foundation stone was laid by Sir Henry Parkes, 18 June 1887. The hospital was opened with accommodation for fourteen patients, with the requisite office and rooms for the medical and nursing staff. Medical staff numbered four honorary doctors and nursing staff numbered five. The site of the original hospital was bounded by Willoughby Rd., Albany and Holterman Streets and Zig Zag Lane. The old site is now a busy part of the commercial centre of Crows Nest.In 1902, it opened on its current site at St Leonards, with 48 beds available for patients. New departments and wards were added over the next fifty years, reflecting the increasing diversity and professionalisation of health care. Between 1935 and 1940, Polio treatment pioneer Sister Kenny Kenny travelled extensively throughout Australia helping to set up clinics. In the mid-thirties, she set up one of her pioneering clinics at RNSH. In 1940, the New South Wales government sent Kenny to America to present her clinical method for treating polio victims to American doctors.